What Causes Mortons Neuroma
Overview
 Interdigital neuroma (Morton?s Neuroma) of the foot includes common, paroxysmal, neuralgia affecting the web spaces of the toes. It involves entrapment neuropathy (nerve compression) of the common digital nerve below and between the metatarsal heads, typically between the third and the fourth metatarsal heads. The pain is most commonly felt between the third and fourth toes but can also occur in the area between the second and third toes.
Interdigital neuroma (Morton?s Neuroma) of the foot includes common, paroxysmal, neuralgia affecting the web spaces of the toes. It involves entrapment neuropathy (nerve compression) of the common digital nerve below and between the metatarsal heads, typically between the third and the fourth metatarsal heads. The pain is most commonly felt between the third and fourth toes but can also occur in the area between the second and third toes.
Causes
Occupational hazards. Individuals whose jobs place undue stress on their forefeet (with or without wearing improper footwear) are among those who complain of neuromas. Podiatric physicians report that individuals who work on ladders, or who perform activities on their knees (such as doing landscaping, carpeting, flooring, or other work on the ground) are at risk for this problem, too, since these activities cause stress to the nerve near the ball of the foot. Those who engage in high-impact activities that bring repetitive trauma to the foot (running, aerobics, etc.) have a better than average chance of developing a neuroma at the site of a previous injury. To put it more simply, if you have sustained a previous injury to your foot (a sprain, stress fracture, etc.), that area of your foot will be more prone to neuroma development than an area that has not been injured. However, sports injuries aren?t automatically a ticket to neuromas. Trauma caused by other forms of injury to the foot (dropping heavy objects, for example) can also cause a neuroma to develop at the site of the previous injury. Much though we hate to say it, sometimes neuromas just develop and nobody knows why. The patient doesn?t have a previous injury, is wearing properly fitted shoes, and doesn?t stress his/her feet with any specific activity but the neuroma develops anyway. It is important to remember that some of the factors listed above can work alone, or in combination with each other, to contribute to the formation of neuroma.
Symptoms
Patients will complain of numbness, a ?pins and needles? type of tingling and loss of sensation in the toes. Burning pain in the ball of the foot that may radiate into the toes. The pain generally intensifies with activity or wearing shoes. Night pain is rare. There may also be numbness in the toes, or an unpleasant feeling in the toes. Runners may feel pain as they push off from the starting block. High-heeled shoes, which put the foot in a similar position to the push-off, can also aggravate the condition. Tight, narrow shoes also aggravate this condition by compressing the toe bones and pinching the nerve.
Diagnosis
X-rays of your affected foot will not show a neuroma, as neuromas are made up of soft tissue. X-rays may be helpful, however, in helping rule in osteoarthritis or a stress fracture as the cause of your symptoms. Ultrasonography and MRI are sometimes used to help diagnose neuromas, although they are often ineffective. The clinical diagnosis by a foot care expert with experience treating this health problem is usually the most effective way to diagnose neuromas. Your podiatrist will attempt to duplicate your neuroma symptoms by pressing on the involved nerve at various points, and he or she may try to cause a clicking of your nerve that indicates nerve enlargement.
Non Surgical Treatment
Relief of symptoms can often start by having a good pair of well fitting shoes fitted to your feet ensuring that the shoes don't squeeze your foot together. Once footwear is addressed patients may require a small pre-metatarsal pad to be positioned onto the insole of the shoe to help lift and separate the bones in the forefoot to alleviate the pressure on the nerve. If the patients foot structure and mechanics is found to be a contributing cause, a custom made orthotic is usually the most convenient and effective way to manage the problem. Sometimes an injection of local anaesthetic and steroid is recommended to assist in settling acute symptoms.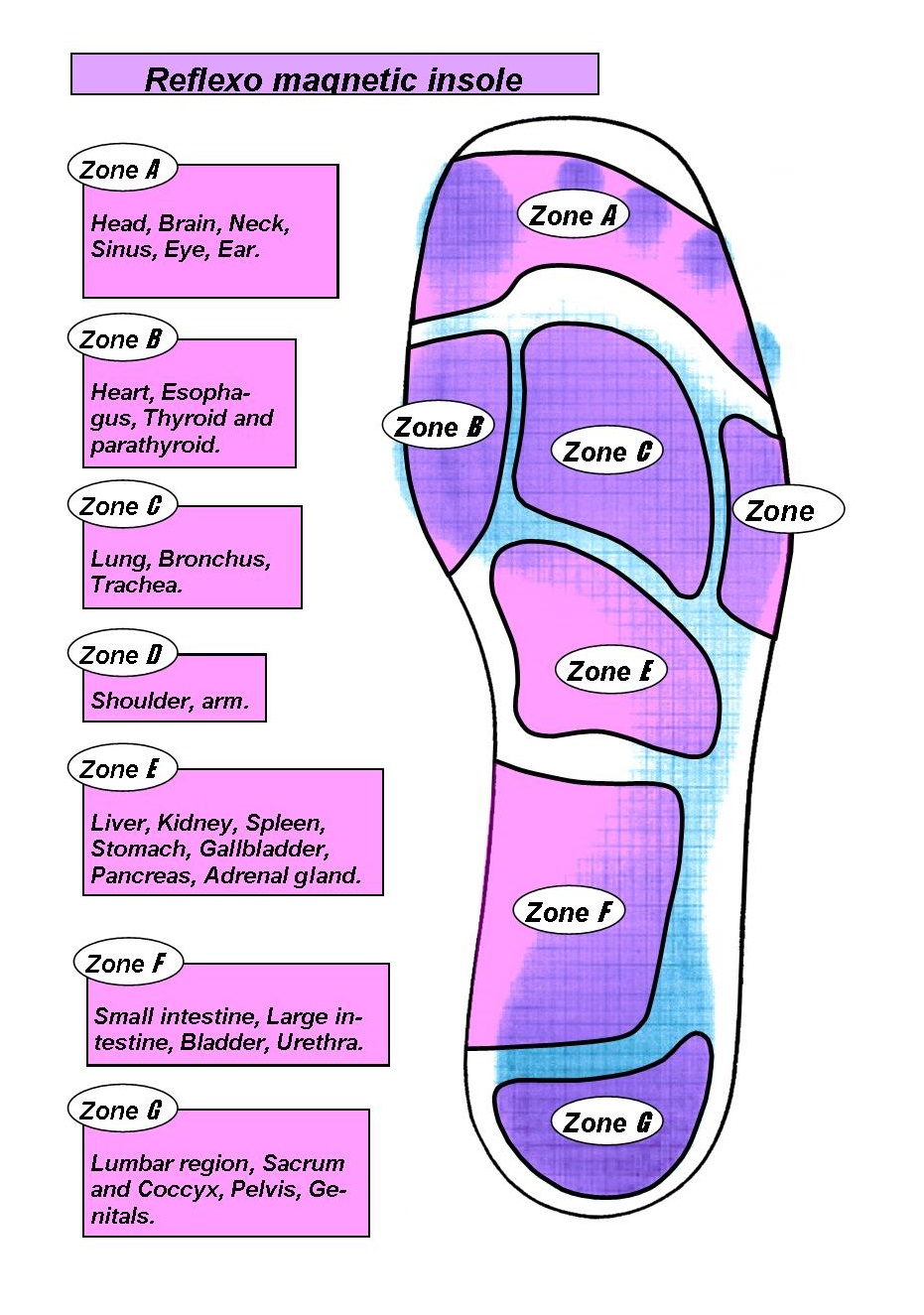
Surgical Treatment
If conservative treatment does not relieve your symptoms, your orthopaedic surgeon may discuss surgical treatment options with you. Surgery can resect a small portion of the nerve or release the tissue around the nerve, and generally involves a short recovery period.
 Interdigital neuroma (Morton?s Neuroma) of the foot includes common, paroxysmal, neuralgia affecting the web spaces of the toes. It involves entrapment neuropathy (nerve compression) of the common digital nerve below and between the metatarsal heads, typically between the third and the fourth metatarsal heads. The pain is most commonly felt between the third and fourth toes but can also occur in the area between the second and third toes.
Interdigital neuroma (Morton?s Neuroma) of the foot includes common, paroxysmal, neuralgia affecting the web spaces of the toes. It involves entrapment neuropathy (nerve compression) of the common digital nerve below and between the metatarsal heads, typically between the third and the fourth metatarsal heads. The pain is most commonly felt between the third and fourth toes but can also occur in the area between the second and third toes.Causes
Occupational hazards. Individuals whose jobs place undue stress on their forefeet (with or without wearing improper footwear) are among those who complain of neuromas. Podiatric physicians report that individuals who work on ladders, or who perform activities on their knees (such as doing landscaping, carpeting, flooring, or other work on the ground) are at risk for this problem, too, since these activities cause stress to the nerve near the ball of the foot. Those who engage in high-impact activities that bring repetitive trauma to the foot (running, aerobics, etc.) have a better than average chance of developing a neuroma at the site of a previous injury. To put it more simply, if you have sustained a previous injury to your foot (a sprain, stress fracture, etc.), that area of your foot will be more prone to neuroma development than an area that has not been injured. However, sports injuries aren?t automatically a ticket to neuromas. Trauma caused by other forms of injury to the foot (dropping heavy objects, for example) can also cause a neuroma to develop at the site of the previous injury. Much though we hate to say it, sometimes neuromas just develop and nobody knows why. The patient doesn?t have a previous injury, is wearing properly fitted shoes, and doesn?t stress his/her feet with any specific activity but the neuroma develops anyway. It is important to remember that some of the factors listed above can work alone, or in combination with each other, to contribute to the formation of neuroma.
Symptoms
Patients will complain of numbness, a ?pins and needles? type of tingling and loss of sensation in the toes. Burning pain in the ball of the foot that may radiate into the toes. The pain generally intensifies with activity or wearing shoes. Night pain is rare. There may also be numbness in the toes, or an unpleasant feeling in the toes. Runners may feel pain as they push off from the starting block. High-heeled shoes, which put the foot in a similar position to the push-off, can also aggravate the condition. Tight, narrow shoes also aggravate this condition by compressing the toe bones and pinching the nerve.
Diagnosis
X-rays of your affected foot will not show a neuroma, as neuromas are made up of soft tissue. X-rays may be helpful, however, in helping rule in osteoarthritis or a stress fracture as the cause of your symptoms. Ultrasonography and MRI are sometimes used to help diagnose neuromas, although they are often ineffective. The clinical diagnosis by a foot care expert with experience treating this health problem is usually the most effective way to diagnose neuromas. Your podiatrist will attempt to duplicate your neuroma symptoms by pressing on the involved nerve at various points, and he or she may try to cause a clicking of your nerve that indicates nerve enlargement.
Non Surgical Treatment
Relief of symptoms can often start by having a good pair of well fitting shoes fitted to your feet ensuring that the shoes don't squeeze your foot together. Once footwear is addressed patients may require a small pre-metatarsal pad to be positioned onto the insole of the shoe to help lift and separate the bones in the forefoot to alleviate the pressure on the nerve. If the patients foot structure and mechanics is found to be a contributing cause, a custom made orthotic is usually the most convenient and effective way to manage the problem. Sometimes an injection of local anaesthetic and steroid is recommended to assist in settling acute symptoms.

Surgical Treatment
If conservative treatment does not relieve your symptoms, your orthopaedic surgeon may discuss surgical treatment options with you. Surgery can resect a small portion of the nerve or release the tissue around the nerve, and generally involves a short recovery period.